NSC800 Conversion: Difference between revisions
| (18 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 92: | Line 92: | ||
All these patches rolled up into a binary: (here I used the T102 base ROM as the starting point) | All these patches rolled up into a binary: (here I used the T102 base ROM as the starting point) | ||
This file here is the original. It works ok but I found an arithmetic bug due to slight difference in how Z80 handles the parity flag. | |||
[[Media:M102_nsc800.zip|M102_nsc800.zip]] | [[Media:M102_nsc800.zip|M102_nsc800.zip]] | ||
As of December 2024, I now use the following image. It has this new patch to support the NSC800 parity flag usage difference. | |||
This was a fun debug; the "error" to fix is actually kinda well known. The original BASIC code was written for 8080 and then re-used in M100 BASIC for 8085. Between 1975 and 1983, the Model 1 was introduced on Z80 and the code was fixed at that time. The patch just did not make it into the M100. Till now! | |||
Here's the original code (RST 5): | |||
LDA 0FB65H ; Type of last variable used | |||
CPI 08d | |||
DCR | |||
DCR | |||
DCR | |||
ret | |||
Here's the patch (thanks to George Phillips): | |||
var_fix: | |||
LDA 0FB65H | |||
CPI 08H | |||
JC var_carry | |||
sui 03d | |||
ora a | |||
RET | |||
var_carry: | |||
sui 03d | |||
ora a | |||
STC | |||
RET | |||
[[Media:M102_nsc800_v2.zip|M102_nsc800_v2.zip]] | |||
These are what I use today. If I find bugs I will post updates. | |||
== Notes on use with M100 CP/M == | == Notes on use with M100 CP/M == | ||
| Line 119: | Line 147: | ||
5. IMPORT and EXPORT are not written using 8080 opcodes, so you will need replacements. See below. | 5. IMPORT and EXPORT are not written using 8080 opcodes, so you will need replacements. See below. | ||
6. If you want to use the BCR Hack for external video over MVT100, you need to (1) change the hack slightly and (2) patch CP/M. See below. | 6. If you want to use the BCR Hack for external video over MVT100, you need to (1) change the hack slightly and (2) patch CP/M. See below. | ||
7. Also note - the utilities for backup/restore of REXCPM also do not work on NSC800. | 7. Also note - the utilities for backup/restore of REXCPM also do not work on NSC800... now resolved! RXCUTN below. | ||
| Line 174: | Line 202: | ||
Transfer these programs using IMP80 (and change .COM to .CO for transfer) into CP/M. | Transfer these programs using IMP80 (and change .COM to .CO for transfer) into CP/M. | ||
Note: | |||
----- | |||
TPDD servers usually only support 6.2 filenames. | |||
John has a version of LaddieAlpha that supports 8.3 filenames, which is ideal for CP/M use. | |||
The end result is that by using this version of LaddieAlpha, and my TD/TS/TL/TK utilities, | |||
you can work directly with 8.3 files. | |||
Contact John directly for a LaddieAlpha that works with 8.3 filenames. | |||
=== How do I get M100 CP/M loaded up? === | === How do I get M100 CP/M loaded up? === | ||
| Line 232: | Line 268: | ||
3. VT100 video over (a suitably modified) BCR port | 3. VT100 video over (a suitably modified) BCR port | ||
With NSC800 processor, since we don't have the SOD | With NSC800 processor, since we don't have the SID or SOD pins nor the RIM/SIM opcodes, the BCR hack needed to change. | ||
That change is documented here: | That change is documented here: | ||
https://bitchin100.com/wiki/index.php?title=BCR_TTL_SERIAL_HACK#NSC800_BCR_Hack | https://bitchin100.com/wiki/index.php?title=BCR_TTL_SERIAL_HACK#NSC800_BCR_Hack | ||
The original hack "V1" uses the SOD pin... not good for NSC800. | |||
A more generic hack "V2" uses the Motor on/off relay control to bit bang the Tx serial data at high speed. | |||
V2 works for both 80C85 and NSC800. | |||
This change requires a bit of software change to work, though. | This change requires a bit of software change to work, though. | ||
| Line 242: | Line 282: | ||
The patched CPM440.bs file posted above includes this patch. | The patched CPM440.bs file posted above includes this patch. | ||
=== How do I back up my CP/M Disk? === | |||
The RXCUTL utility provided with REXCPM software unfortunately does not run on NSC800. | |||
A new version called RXCUTN does however. It works the same as RXCUTL. | |||
NOTE: | |||
Backups generated by RXCUTL are not compatible with RXCUTN. | |||
Please create new backups using RXCUTN. | |||
RXCUTN | |||
* supports NSC800 or 8085 | |||
* runs on 2.5 or 5.0 MHz clock speeds | |||
* provides backup or restore for REXCPM on-board storage. | |||
* can be used to backup/restore either the M100 memory region of REXCPM OR the CP/M memory region | |||
* runs at 19200 or 76800 baud | |||
Some of the REXCPM SRAM is dedicated to CP/M while other memory is dedicated to REX functionality. | |||
Backup and restore of either the REX side or the CP/M side gives the user a means to create complete images of the memory over time, so if needed the machine can be brought back to the desired state. | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|'''Software'''||'''Version'''||'''Note'''||'''File''' | |||
|- | |||
|RXCUTN|| 3 || initial release December 2024 ||[[Media:RXCUTN.ZIP|RXCUTN.ZIP]] | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
Notes: | |||
====== | |||
* current version is version 3. | |||
* Either a Backup or Restore process | |||
* REXCPM or CP/M memory regions | |||
REXCPM memory includes REXCPM ROM image + directory + 16 blocks | |||
Total of 17 32kB blocks. | |||
CP/M memory includes all of the CP/M disk space, including directory (but excluding CP/M OS) | |||
For 2MB, 40 32kB blocks. For 4MB, 104 32kB blocks. | |||
* Serial port speed - 19200 8N1 or 76800 8N1 | |||
* If you get the message "CAN'T RUN" | |||
---> please remove the REX hook (CNTL-X or F7) | |||
---> power cycle | |||
---> and try again | |||
The tool uses the standard RS-232 port on the M100. Standard TPDD servers can operate at 19200 baud, but LaddieAlpha is capable of operation at 76800 baud, and also able to support large packet sizes, both of which help to speed up the process. | |||
NOTE: LaddieAlpha with 76800 baud support is not generally available yet. Stay tuned. | |||
Backup/Restore processes can take some time; use this table for guidance. | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|'''Process'''||'''Memory size'''||'''Duration'''||'''Duration''' | |||
|- | |||
|REXCPM||either||19200||5:20 min | |||
|- | |||
|CP/M||2MB||19200||13 min | |||
|- | |||
|CP/M||4MB||19200||33 min | |||
|- | |||
|REXCPM||either||76800||2:10 min | |||
|- | |||
|CP/M||2MB||76800||5 min | |||
|- | |||
|CP/M||4MB||76800||13:15 min | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
Instructions | |||
============ | |||
1. Make sure REXCPM is in default state, meaning | |||
a. RXCMGR is not running (use CNTL-X to remove hooks, or F7 from RXCMGR) | |||
b. Power cycle once, to ensure the default memory blocks are selected | |||
c. Optionally, cold-rebooting the laptop after a power cycle ensures a clean state. | |||
2. load RXCUTN.DO into the M100 using a terminal program on PC (lots of ways to do this) | |||
It is 7 bit ASCII. RXCULN.DO contains HEX ASCII encoded machine language. | |||
3. Enter BASIC and type RUN"RXCUTN.DO" | |||
4. Select Process, REX or CP/M, and speed | |||
5. The loader will load up the machine language routine, and begin to execute | |||
6. Ensure that a TPDD server is attached to the serial port | |||
7. For either process, supply 6 character case-sensitive name for the file. | |||
File extension is set to .BB | |||
8. Once executed, RXCUTN will attempt to either write or read all required data to/from REXCPM SRAM. | |||
Note: | |||
===== | |||
If you see an error message - "CAN'T RUN", this means that REXCPM is not in the default state. | |||
See instruction #1 above! | |||
=== Setting up your system for 76800 baud === | |||
To run backup/restore at 76800 baud, you need a couple of things. | |||
1) a serial port capable of 76800 baud | |||
2) a TPDD server that is able to run at 76800 baud | |||
Regarding serial port, what I use is a USB serial port based on the FTDI chip. | |||
An example of an FTDI based USB serial port is here: | |||
https://www.startech.com/en-ca/cards-adapters/icusb2321f | |||
However, 76800 is not a standard baud. So, you generally have to make some changes to your host machine and the change is different depending on the operating system. | |||
This article provides a good summary: | |||
https://sourceforge.net/p/bacnet/discussion/402140/thread/f2eeb911/ | |||
For Windows, you edit the registry to provide an alternative dividsor value, to enable 76800. | |||
Here's the good part for Windows: | |||
Windows XP | |||
1) Plug in and locate your USB/RSS85 in Device Manager under ports. Right | |||
click on it and select Properties. Click Details tab and from the drop down | |||
select Device Instance Id. | |||
2) Click Start, Run and then type regedit. | |||
Follow this path in the registry | |||
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Enum\FTDIBUS | |||
Locate the folder that has the same name as what you found earlier Device | |||
Instance Id in step 1. Click on 0000 folder and then Device Parameters. On the | |||
right side you will see ConfigData. Right click and select Modify Binary Data. | |||
Locate the 10 27 which in my case were in 5th and 6th position and replace | |||
with 27 C0. | |||
This will make the RS485 go to 76800 baud (76923 baud) baud when you ask it to | |||
be 300 baud. | |||
So to capture at 76800 baud type: mstpcap.exe COM2 300 | |||
With regards to a TPDD server, I use a version of LaddieAlpha which John has modified to allow serial port parameters to be set. | |||
I suggest contacting John with regards to getting an up-to-date LaddieAlpha that supports baud rate settings. | |||
=== Is there a quick way to bootstrap my CP/M system from scratch? === | |||
Why yes there is. | |||
Use RXCUTN to "restore" a working CP/M image directly into your REXCPM. | |||
Then, load and run CPM.DO to allow you to start CP/M. | |||
Just for kicks, here is my current NSC800 CP/M disk image. | |||
Contains Turbo Pascal, MBASIC, maybe BDS-C, my TPDD utilities, etc. | |||
[[ | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|'''Software'''||'''Version'''||'''Note'''||'''File''' | |||
|- | |||
|NSC800 disk image|| 2MB image || as of December 2024 ||[[Media:NSC800_disk.ZIP|NSC800_disk.ZIP]] | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
Latest revision as of 06:15, 26 December 2024
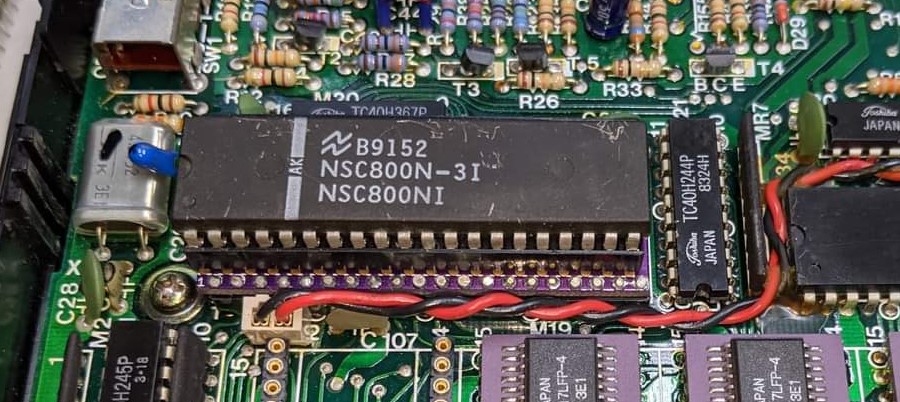
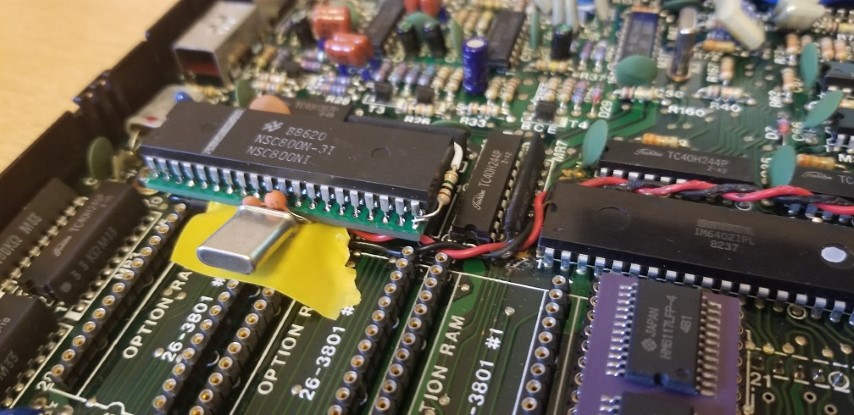
Protytype!
Current version! (courtesy John Wiggins)
What is this all about?
Motivated by 2 things
- discovery (to me) of the NSC800 Z80 processor that is 80C85 like
- continuing to work in the direction of CP/M
I have invested some time and effort in developing a conversion that supports NSC800 operation in the M100, both for standard BASIC use, as well as CP/M (in conjunction with REXCPM). Partly this has been motivated simply by curiosity. However, in CP/M it actually broadens the software applicability since quite a bit of CP/M software is Z80.
If you have an interested in doing this conversion please get in touch with me at Twospruces at --the google mail service.
What are the tradeoffs?
When installed, you get an M100 that is ALMOST exactly the same. Differences:
1. Z80 not 80C85...ok
2. Still runs the same BASIC applications
3. Cassette port no longer works as the 80C85 uniquely has the SID/SOD pins but NSC800 does not.
4. NSC800 is NOT COMPATIBLE with REXMGR software, so you can't benefit from the standard REX features when using NSC800.
5. almost 100% compatible with M100 software, even machine code. Except for:
* anything that makes use of the hardware interrupts - Timer, RS-232, BCR port - may require a patch to work.
6. When combined with REXCPM, you get to run Z80 software in M100 CP/M! See below section on M100 CP/M use.
The NSC800 processor uses the interrupts in a slightly different way, so machine code that uses the interrupts needs to change a bit. Patches need to be applied to the M100 Main ROM (see below) to tweak things a bit to work.
Required Changes
There are 2 areas of change that are needed. Firstly you have to adapt the NSC800 to the 80C85 socket. There are a couple of tradeoffs to make. Secondly, the NSC800 needs to use a slightly different Main ROM.
To get started on this project, one can leverage the work done in the past. In fact an NSC800 conversion for 80C85 was posted back in the early 80s for S100 computers equipped with an 8080/8085 processor board. The information is posted below, from Microsystems September 1984.
This article lists considerations; from my work in M100 the things that any adapter has to deal with are listed below.
1. Inversion of the interrupt signals 2. Conversion of the 50/50 duty cycle RST7.5 signal to a 100 usec low pulse (NSC800 is level triggered not edge). 3. 4.9152 MHZ clock generation circuitry. 4. And in the case of a dual processor conversion, certain NSC800 signals are not tri-state in RESET.
Note: it seems that the M100 RAM/ROM and REX are all tolerant of the short opcode fetch read/write cycle. So, no wait state generator appears to be needed.
A single NSC800 CPU conversion is what is available today. I am working on a dual CPU conversion as well.
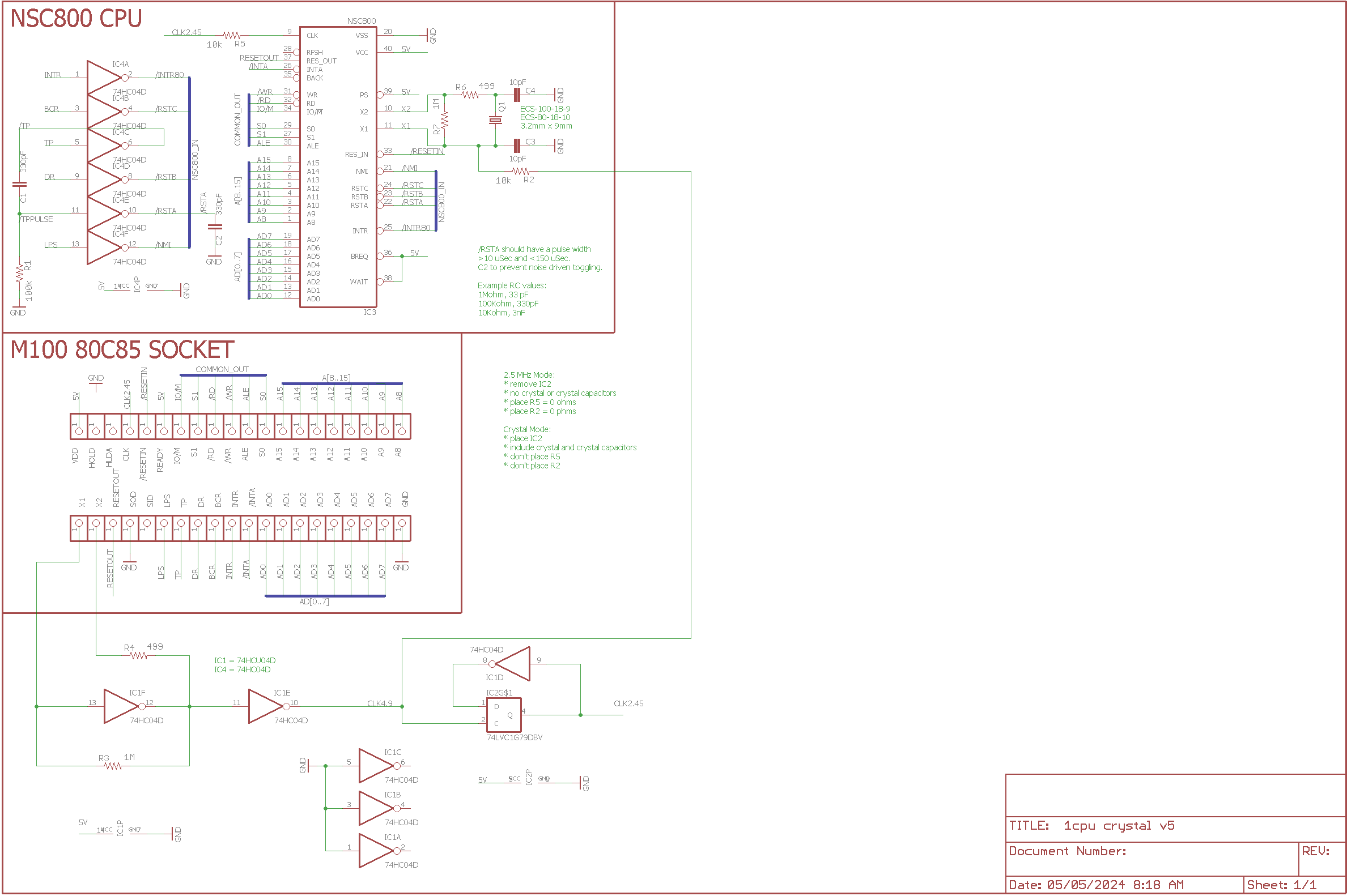
The single NSC800 conversion design has gone through 4 revisions and is now at V5.
* designed for 5MHz operation * assumes REXCPM is providing all SRAM needed (so the RAM is fast enough) * assumes there is a suitably fast M100 patched main ROM installed * can be configured to run at 2.5MHz if required
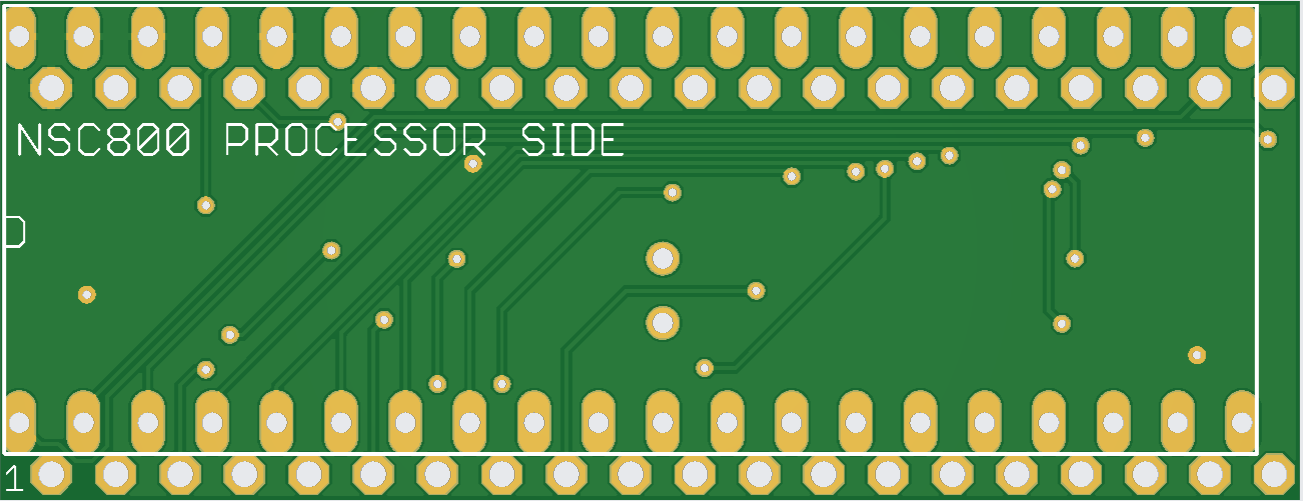
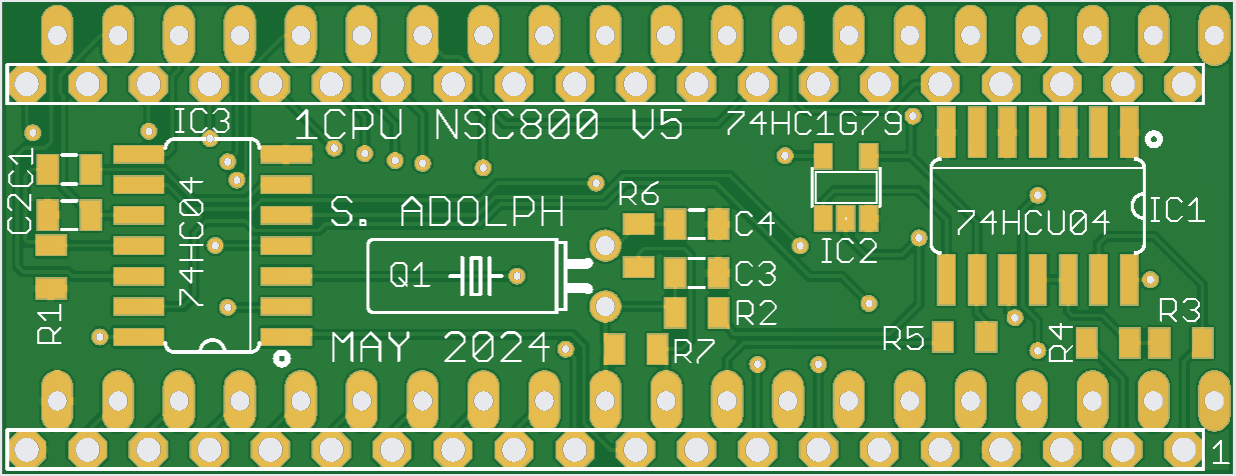
1CPU NSC800 conversion PCB
The V5 schematic is here.
PCB images are below.
Modified M100 Main ROM
As mentioned, since the interrupt control mechanisms in NSC800 are slightly different, the M100 main ROM needs to be patched to support NSC800.
The NSC800 patch needs extra code space to be created in the ROM. To do that, an original patch has been verified that creates a block of unused space in the main ROM as published by Microsoft.
Once this base patch is applied to the ROM, you have space now for the next set of patches, here.
All these patches rolled up into a binary: (here I used the T102 base ROM as the starting point)
This file here is the original. It works ok but I found an arithmetic bug due to slight difference in how Z80 handles the parity flag.
As of December 2024, I now use the following image. It has this new patch to support the NSC800 parity flag usage difference. This was a fun debug; the "error" to fix is actually kinda well known. The original BASIC code was written for 8080 and then re-used in M100 BASIC for 8085. Between 1975 and 1983, the Model 1 was introduced on Z80 and the code was fixed at that time. The patch just did not make it into the M100. Till now!
Here's the original code (RST 5):
LDA 0FB65H ; Type of last variable used CPI 08d DCR DCR DCR ret
Here's the patch (thanks to George Phillips):
var_fix: LDA 0FB65H CPI 08H JC var_carry sui 03d ora a RET var_carry: sui 03d ora a STC RET
These are what I use today. If I find bugs I will post updates.
Notes on use with M100 CP/M
Probably, you have installed an NSC800 processor and supporting M100/T102 main ROM, so that you can use M100 CP/M and gain the benefit of Z80. I suppose to be fair it is possible to run the NSC800 in the laptop, and yes it would be a Z80 - so you could write new programs that are based on Z80 opcodes. Not sure that would be worth it.
So, how does one get M100 CP/M rolling with the NSC800? CP/M 2.2 is generally based on 8080, so the operating system itself is fine. Well you for sure need a REXCPM, either 2MB or 4MB. I will assume that you would have already been familiar with setting up M100 CP/M using the standard config with 80C85 installed.
There are a few major considerations.
1. RXCMGR software does NOT support NSC800! RXCMGR makes extensive use of the 80C85 undocumented opcodes, so it won't run on NSC800. 2. Installing and running CP/M relies solely on the tools provided for M100 CP/M. 3. In order to load up the M100 CP/M utilities, you will need a DOS of some kind. See below. 4. M100 CP/M, as it comes in standard form, IS generally compatible with NSC800. 5. IMPORT and EXPORT are not written using 8080 opcodes, so you will need replacements. See below. 6. If you want to use the BCR Hack for external video over MVT100, you need to (1) change the hack slightly and (2) patch CP/M. See below. 7. Also note - the utilities for backup/restore of REXCPM also do not work on NSC800... now resolved! RXCUTN below.
How do I transfer files into the laptop?
TELCOM application in M100 still works with M100. So, any .DO file is loadable using the standard methods with TELCOM.
But why? What about the interrupt issue? ... in the modified T102 main rom, I have patched it up so that the serial port still works correctly. The T102 main rom provides routines for getting and sending data over RS-232 and those routines work fine. However, any serial port software that uses POLL MODE will not work correctly as the NSC800 does not have an opcode like SIM/RIM. --> so as a general rule I would say - assume that serial port and BCR port work fine with NSC800, but it is possible that 3rd party software might try to POLL the interrupt status and that could cause a problem. Try first, and decide.
NTEENY for M100 mode
TELCOM alone does not solve the problem, since .CO and .BA programs are not text. What to do? Well, what about TEENY? TEENY happens to make use of SIM opcode unfortunately. So, I have built on the great work of Ron Wiesen, and modified TEENY to run on NSC800.
I have been using NTEENY below and do not observe any problems, but please do report back if you find any issues. This is for NSC800 only, please use standard TEENY on 80C85.
Version 1 loads and runs NTEENY directly. Get the CO via SAVEM"NTEENY.CO",62213,62960,62213
Version 2 creates NTEENY.CO
This is not as fancy as Ron's because it loads and runs at a fixed location 62213, but it should suffice.
TPDD Utilities for CP/M mode
I wrote some CP/M utilities for directly accessing a TPDD (like an actual TPDD, or LaddieAlpha) from CP/M. These programs assume files are named with 8.3 format in both the TPDD and of course CP/M.
TD.COM: TPDD directory TS.COM: Save file to TPDD TL.COM: Load file from TPDD TK.COM: Kill file on TPDD (soon to come: TCD.COM: TPDD change directory)
Transfer these programs using IMP80 (and change .COM to .CO for transfer) into CP/M.
Note: ----- TPDD servers usually only support 6.2 filenames. John has a version of LaddieAlpha that supports 8.3 filenames, which is ideal for CP/M use. The end result is that by using this version of LaddieAlpha, and my TD/TS/TL/TK utilities, you can work directly with 8.3 files. Contact John directly for a LaddieAlpha that works with 8.3 filenames.
How do I get M100 CP/M loaded up?
The best way to get M100 CP/M running with NSC800 is to start with a known good M100 CP/M installation, and then convert the hardware.
The currently posted version of M100 CP/M happens to use 8085 undocumented opcodes. A modified version of M100 CP/M has been prepared that is pure 8080.
This version of M100 CP/M includes the following changes 1. all 8085 undoc opcodes have been removed, and the code reworked. 2. a patch has been applied to support the NSC800 version of the BCR hack.
Because stock IMPORT/EXPORT don't work with the NSC800, that problem needs to be solved BEFORE you install the NSC800 CPU.
I modified Philip's IMPORT and EXPORT routines to eliminate the 80C85 undoc opcodes and SIM/RIM. The result are 8080 based versions called IMP80 and EXP80, below.
Steps to get M100 CP/M and NSC800 running:
0. Modify the M100 to put a socket in place where the 80C85 is. Install the 80C85 for now.
1. Start with a freshly installed REXCPM in an M100, with no CP/M installed. So, a blank REXCPM.
2. Follow Philip's procedures to get an initial M100 CP/M system up and running. Use the posted files.
3. Run M100 CP/M from the laptop LCD, not RS-232 or CASS (BCR).
4. Using IMPORT, transfer into CP/M the modified IMP80 and EXP80. Test that they work as expected.
5. Update M100 CP/M to use CPM440_patched.bs, by using CPMUPD.CO. Change the filename to CPM440.bs.
Switch back to M100 mode. Run the command CPMUPD.CO CPM440.bs
This will update the CP/M operating system.
OK, now you have a system ready to transplant the NSC800. Next..
6. Open the M100, and install (1) the NSC800 and (2) the modified main ROM. 7. Close up the laptop, and power up. You should see that the NSC800 is working. 8. Now, start CP/M and you should be up and running.
Since the NSC800 and RXCMGR are incompatible, use CPM.CO to start CP/M.
For added convenience, I have made a version of CPM.CO as a .DO file, for easy file transfer to the laptop. Use this if your CPM.CO file gets corrupted.
Comments welcome on this procedure!
What about using the BCR Hack for external video?
Ah, great question! As you know M100 CP/M supports 3 types of video
1. M100 native LCD 2. VT100 video over RS-232 3. VT100 video over (a suitably modified) BCR port
With NSC800 processor, since we don't have the SID or SOD pins nor the RIM/SIM opcodes, the BCR hack needed to change. That change is documented here:
https://bitchin100.com/wiki/index.php?title=BCR_TTL_SERIAL_HACK#NSC800_BCR_Hack
The original hack "V1" uses the SOD pin... not good for NSC800. A more generic hack "V2" uses the Motor on/off relay control to bit bang the Tx serial data at high speed. V2 works for both 80C85 and NSC800.
This change requires a bit of software change to work, though. To make M100 CP/M send video data over this modified BCR hack, a patch is needed.
The patched CPM440.bs file posted above includes this patch.
How do I back up my CP/M Disk?
The RXCUTL utility provided with REXCPM software unfortunately does not run on NSC800. A new version called RXCUTN does however. It works the same as RXCUTL.
NOTE: Backups generated by RXCUTL are not compatible with RXCUTN. Please create new backups using RXCUTN.
RXCUTN * supports NSC800 or 8085 * runs on 2.5 or 5.0 MHz clock speeds * provides backup or restore for REXCPM on-board storage. * can be used to backup/restore either the M100 memory region of REXCPM OR the CP/M memory region * runs at 19200 or 76800 baud
Some of the REXCPM SRAM is dedicated to CP/M while other memory is dedicated to REX functionality.
Backup and restore of either the REX side or the CP/M side gives the user a means to create complete images of the memory over time, so if needed the machine can be brought back to the desired state.
| Software | Version | Note | File |
| RXCUTN | 3 | initial release December 2024 | RXCUTN.ZIP |
Notes:
======
* current version is version 3.
* Either a Backup or Restore process
* REXCPM or CP/M memory regions
REXCPM memory includes REXCPM ROM image + directory + 16 blocks
Total of 17 32kB blocks.
CP/M memory includes all of the CP/M disk space, including directory (but excluding CP/M OS)
For 2MB, 40 32kB blocks. For 4MB, 104 32kB blocks.
* Serial port speed - 19200 8N1 or 76800 8N1
* If you get the message "CAN'T RUN" ---> please remove the REX hook (CNTL-X or F7) ---> power cycle ---> and try again
The tool uses the standard RS-232 port on the M100. Standard TPDD servers can operate at 19200 baud, but LaddieAlpha is capable of operation at 76800 baud, and also able to support large packet sizes, both of which help to speed up the process.
NOTE: LaddieAlpha with 76800 baud support is not generally available yet. Stay tuned.
Backup/Restore processes can take some time; use this table for guidance.
| Process | Memory size | Duration | Duration |
| REXCPM | either | 19200 | 5:20 min |
| CP/M | 2MB | 19200 | 13 min |
| CP/M | 4MB | 19200 | 33 min |
| REXCPM | either | 76800 | 2:10 min |
| CP/M | 2MB | 76800 | 5 min |
| CP/M | 4MB | 76800 | 13:15 min |
Instructions
============
1. Make sure REXCPM is in default state, meaning
a. RXCMGR is not running (use CNTL-X to remove hooks, or F7 from RXCMGR)
b. Power cycle once, to ensure the default memory blocks are selected
c. Optionally, cold-rebooting the laptop after a power cycle ensures a clean state.
2. load RXCUTN.DO into the M100 using a terminal program on PC (lots of ways to do this)
It is 7 bit ASCII. RXCULN.DO contains HEX ASCII encoded machine language.
3. Enter BASIC and type RUN"RXCUTN.DO"
4. Select Process, REX or CP/M, and speed
5. The loader will load up the machine language routine, and begin to execute
6. Ensure that a TPDD server is attached to the serial port
7. For either process, supply 6 character case-sensitive name for the file.
File extension is set to .BB
8. Once executed, RXCUTN will attempt to either write or read all required data to/from REXCPM SRAM.
Note: ===== If you see an error message - "CAN'T RUN", this means that REXCPM is not in the default state. See instruction #1 above!
Setting up your system for 76800 baud
To run backup/restore at 76800 baud, you need a couple of things.
1) a serial port capable of 76800 baud 2) a TPDD server that is able to run at 76800 baud
Regarding serial port, what I use is a USB serial port based on the FTDI chip.
An example of an FTDI based USB serial port is here: https://www.startech.com/en-ca/cards-adapters/icusb2321f
However, 76800 is not a standard baud. So, you generally have to make some changes to your host machine and the change is different depending on the operating system.
This article provides a good summary: https://sourceforge.net/p/bacnet/discussion/402140/thread/f2eeb911/
For Windows, you edit the registry to provide an alternative dividsor value, to enable 76800.
Here's the good part for Windows: Windows XP 1) Plug in and locate your USB/RSS85 in Device Manager under ports. Right click on it and select Properties. Click Details tab and from the drop down select Device Instance Id. 2) Click Start, Run and then type regedit. Follow this path in the registry HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Enum\FTDIBUS Locate the folder that has the same name as what you found earlier Device Instance Id in step 1. Click on 0000 folder and then Device Parameters. On the right side you will see ConfigData. Right click and select Modify Binary Data. Locate the 10 27 which in my case were in 5th and 6th position and replace with 27 C0. This will make the RS485 go to 76800 baud (76923 baud) baud when you ask it to be 300 baud. So to capture at 76800 baud type: mstpcap.exe COM2 300
With regards to a TPDD server, I use a version of LaddieAlpha which John has modified to allow serial port parameters to be set.
I suggest contacting John with regards to getting an up-to-date LaddieAlpha that supports baud rate settings.
Is there a quick way to bootstrap my CP/M system from scratch?
Why yes there is.
Use RXCUTN to "restore" a working CP/M image directly into your REXCPM. Then, load and run CPM.DO to allow you to start CP/M.
Just for kicks, here is my current NSC800 CP/M disk image.
Contains Turbo Pascal, MBASIC, maybe BDS-C, my TPDD utilities, etc.
| Software | Version | Note | File |
| NSC800 disk image | 2MB image | as of December 2024 | NSC800_disk.ZIP |